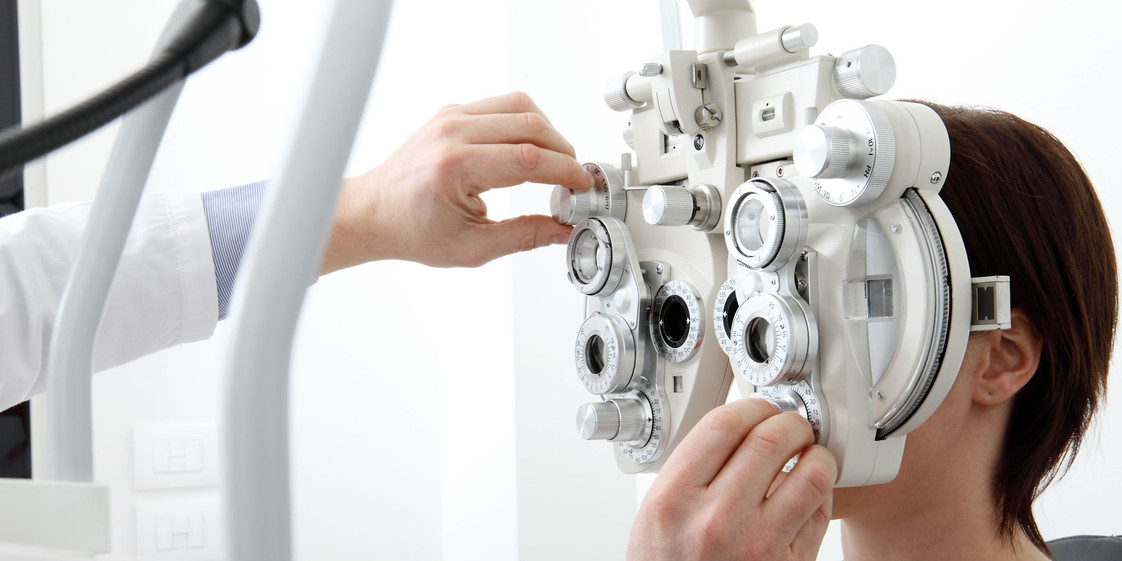
How Long Does an Eye Exam Take: Duration and Process Breakdown
Posted by Team Debby on 14th Apr 2024
How Long Does an Eye Exam Take: Duration and Process Breakdown
When scheduling an eye exam, one of the first questions we often ask is how long the process will take.
The duration of an eye exam can vary depending on several factors, such as the reason for the exam, whether it's a routine check-up or a diagnostic procedure, and the type of tests the eye care professional plans to perform.
Generally, a comprehensive eye exam can take anywhere from 30 to 60 minutes. If further testing is needed, the appointment could last longer.

During an eye exam, we undergo a series of tests designed to evaluate our vision and check for eye diseases.
Our eye care provider will start with questions about our visual history and any current symptoms. Then they'll proceed with tests to measure visual acuity, assess our prescription needs, and examine the health of our eyes.
Additional tests for depth perception, color vision, and the response of pupils may also be included.
We should prepare for our eye exam by allotting enough time so that the optometrist or ophthalmologist can perform a thorough assessment.
If it's our first visit or if we're due for a more in-depth evaluation, it might be wise to allow extra time beyond the typical one-hour window. This ensures that we're not rushed and that all necessary tests can be completed for a comprehensive understanding of our eye health.
Understanding Eye Exams

We understand that maintaining optimal eye health is essential. Regular comprehensive eye exams are vital for the early identification and treatment of eye disorders.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are crucial for ensuring the health of your vision and eyes. By scheduling routine check-ups, we can detect eye diseases and vision issues early on, which can lead to more effective treatments.
These exams are necessary regardless of your age or physical health, as some eye disorders may not show symptoms initially.
- Medical history review: Our optometrists review any history of eye conditions, medications, and overall health to personalize your examination.
- Vision tests: These assess how clearly each eye is seeing through various methods, including reading eye charts.
- Eye functionality tests: We evaluate depth perception, color vision, eye muscle movements, peripheral vision, and how pupils respond to light.
What is a Comprehensive Eye Exam?
A comprehensive eye exam involves a series of tests conducted by an eye doctor to evaluate your vision and check for eye diseases.
Each test during a comprehensive eye exam assesses a different aspect of your eye health.
- Visual Acuity Test: This measures the sharpness of your vision using an eye chart.
- Eye Health Evaluation: We may use several instruments, aim bright lights directly at your eyes, and request that you look through an array of lenses. These tests assess the health of your eye's interior and exterior.
- Discussion of Findings: After analyzing your test results, we discuss any relevant findings or potential eye disorders and consider the next steps for maintaining or improving your eye health.
Before Your Visit
Before heading to your eye exam, there are a few key steps we need to take to ensure the process is smooth and efficient.
Scheduling an Appointment
To schedule an eye exam, we should start by finding a reputable optometrist or ophthalmologist with availability that matches our schedule.
It's essential to consider our availability during the clinic's operating hours and if we prefer a particular day of the week. After choosing a provider, we can either schedule our appointment over the phone or, if available, use the provider's online booking system.
- Call the clinic: Confirm hours and book a time.
- Online appointment: Use the provider’s website to select a date and time.
Key Information to Provide:
- Preferred dates and times
- Reason for the visit (routine checkup, vision problems, etc.)
- Current contact lenses or glasses prescription
Pre-Appointment Checklist
Before attending our scheduled eye exam, we must gather necessary information and items to bring with us.
This will include a list of current medications and relevant medical history.
Checklist:
- Medical History: Note any major health issues, as they can affect vision.
- Family History of Eye Disease: Be aware of any eye diseases common in our family, like glaucoma or macular degeneration.
- Current Medications: List all that we're currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs.
- Current Eyewear: Bring our glasses, contact lenses, and any prescription details.
For Contact Lens Wearers:
- It's helpful to wear our contact lenses to the appointment and bring our glasses along, ensuring we're comfortable in case our eyes need to rest after the exam.
During the Exam

When we step into an eye exam, we engage in a series of steps designed to thoroughly evaluate our vision and eye health.
These tests assess everything from the basic visual acuity to the more complex eye health factors.
Initial Assessments
We begin our eye exam with Initial Assessments, which set the baseline for our visual capabilities.
- Visual Acuity Test: We start with this fundamental test to determine how well we can see at various distances. It's essential to determine the prescription for glasses or contact lenses.
- Color Vision Test: We check our ability to differentiate colors accurately, identifying any color vision deficiencies.
- Cover Test: This simple procedure assesses how our eyes work together and can indicate strabismus or other binocular vision issues.
Core Vision Tests
In the Core Vision Tests section, we focus on the key functions of our eyes.
- Refraction: This determines our exact lens prescription. Through a machine called a phoropter, we are presented with a series of lens choices to find the clearest vision.
- Glaucoma Test: Tonometry measures the pressure inside our eyes with a gentle puff of air or a pressure-sensitive tip (tonometer) to check for glaucoma risks.
| Part Tested | Test Conducted | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Cornea and Lens | Pupil Dilation | To examine the health of our lens and check for cataracts. |
| Retina and Optic Nerve | Retinal Imaging | To detect conditions like macular degeneration or changes in the optic nerve. |
Eye Health Evaluation
During the Eye Health Evaluation, we examine the structures of the eye in detail.
- Pupil Dilation: By dilating our pupils with special drops, the ophthalmologist gets a better view of the internal structures, such as the lens, retina, and optic nerve.
- Visual Field Test: We assess our peripheral vision, which can identify issues beyond the central visual field. This is especially important for detecting glaucoma.
- Ocular Examination: The health of our eyelids, iris, and other ocular structures is checked, usually with a slit-lamp microscope, to ensure everything is functioning properly.
Potential Additional Tests

In addressing more specific eye concerns, we may recommend further testing beyond the standard examination procedures.
Specialized Testing for Disorders
For patients with suspected ocular disorders such as amblyopia (lazy eye) or strabismus (misalignment of the eyes), ocular motility tests are indispensable. These tests assess the movement and coordination of the eyes and help us determine the best course of treatment.
- Color blindness is evaluated using simple, yet effective tests like the Ishihara test to assess the patient's ability to differentiate colors accurately.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test allowing us to view cross-sections of the retina, providing crucial information about the back of the eye and assisting in the diagnosis of diseases like diabetic retinopathy.
- Topography gives us a detailed map of the cornea's curvature and is particularly useful in diagnosing and managing conditions like astigmatism.
- Fluorescein angiography aids in diagnosing retinal and choroidal diseases by providing a photographic view of blood flow in the retina.
- Through retinal imaging, we attain detailed images critical for the early detection and management of various retinal diseases.
Understanding Your Results
After completing an eye exam, it's crucial to comprehend what the findings signify for your visual health and what steps we need to take next.
Prescriptions and Recommendations
Prescription Details: We will review your prescription measurements, if necessary, which may include spherical (for myopia or hyperopia), cylindrical (for astigmatism), and axis values.
These are critical for crafting your glasses or contact lenses to correct refractive errors and provide clear vision.
- Glasses and Contact Lenses: If corrective lenses are needed, we discuss the benefits of glasses versus contact lenses, considering your lifestyle and preferences.
- Progressive Lenses: For presbyopia, progressive lenses might be recommended to manage the decrease in near vision.
- Updates: It is common for prescriptions to change over time, so we ensure that you have the most up-to-date correction for optimal vision.
Health and Treatment Discussions
Eye Health Review: We examine the health of your eyes, checking for signs of diseases like glaucoma, macular degeneration, and cataracts.
Identifying risk factors, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, is a crucial part of this discussion since these can significantly impact eye health.
- Treatment Plans:
- Diseases: If signs of eye diseases are present, we outline a treatment plan that may include further testing, monitoring, eye drops, or medications.
- Risk Management: We address how to manage and treat risk factors through lifestyle changes or medication to preserve eye health.
- Follow-ups: Scheduling necessary follow-ups helps us monitor conditions like glaucoma, where pressure inside the eye can lead to damage if not managed properly.
By following through with the prescribed recommendations and treatment plans, we can work together to ensure the continued health and clarity of your vision.
Post-Exam Considerations

Upon completion of an eye exam, we determine our next steps based on the results. This includes scheduling any necessary follow-ups and selecting the appropriate eyewear if needed.
Follow-Up and Next Steps
After completing the eye tests, if we detect any symptoms of eye disorders or diseases, such as irregularities with the eyelids or changes in visual acuity, we may need to schedule a follow-up exam.
A standard timeline for a follow-up can vary; if issues are detected, we might schedule an exam sooner than the typical annual eye exam. Here's what our follow-up planning might look like:
- Immediate Follow-Up: If severe symptoms or potential eye diseases are detected, we must schedule a follow-up within 1-2 weeks.
- Routine Follow-Up: For standard eye health, we'll plan our next eye exam in approximately 12 months.
Choosing Eyewear
In the instance a new prescription is needed, we proceed with fitting for glasses or contacts. The right fit is crucial for optimal vision and comfort. Here is how we approach this process:
- Eyeglasses:
- Frame Selection: We choose a frame that complements our face shape and fits our lifestyle needs.
- Lens Options: Depending on our daily activities, options like anti-glare coatings or transitional lenses for sunglasses may be suggested.
- Contacts:
- If opting for contact lenses, a separate contact lens exam could be necessary to ensure the correct fit and prescription.
- We choose the type of contacts, such as daily disposable or extended wear, based on our preferences and eye health.
Selecting eyewear is a detailed process that considers both aesthetic preferences and functional needs, ensuring that we walk away with glasses or contacts that not only help us see better but fit seamlessly into our lives.
Eye Health and Prevention

Maintaining eye health is a proactive measure, and regular eye exams are vital for the prevention of vision issues and eye diseases. We'll explore how to achieve long-term eye health and address age-specific concerns.
Long-Term Health Maintenance
We can preserve our vision through several methods, and routine vision tests are foundational. Consistent screening can detect early signs of eye disorders, such as diabetes-related damage to blood vessels in the eyes.
- Sunglasses: Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays can protect against cataracts and macular degeneration.
- Diabetes and Eye Health: Regular eye exams can reveal diabetes-related eye issues, and controlling blood sugar is crucial for preventing diabetic retinopathy.
- Risk Factors: Keeping tabs on family history and understanding our genetic risk factors can inform the frequency of our eye screenings.
- Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can damage retinal blood vessels, so maintaining a healthy blood pressure is crucial for eye health.
Age-Specific Concerns
The necessity for eye exams increases with age, specifically after reaching age 40, as the risk for age-related eye diseases rises.
- Seniors: For seniors, we recommend annual eye exams to check for age-related macular degeneration and other senior-related eye conditions.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration: This is a common condition in the elderly, and its early detection through eye exams is critical for slowing progression.
- Annual Eye Exams: After 40, we should have our eyes examined yearly, or as recommended, to identify any emerging issues promptly.
By adhering to these guidelines, we contribute to our overall health and safeguard one of our most valuable senses – our sight.
Common Questions and Answers

How long does a typical eye exam take?
An eye exam usually lasts from 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of tests involved.
What tests are included in a routine eye exam?
Tests often include visual acuity, refraction tests for glasses or contact lenses, pupil dilation, ocular motility to assess eye movement, and others that check for glaucoma and retina health.
Will I need someone to drive me home?
If your pupils are dilated during the exam, it could affect your vision temporarily. It's wise to have a ride since it may take a few hours for the effects of the eye drops to wear off.
Can I go back to work after an eye exam?
It's generally fine, but if your job requires sharp vision immediately or if you've had your pupils dilated, you might experience difficulty focusing your eyes for a short time.
What symptoms should prompt us to schedule an eye exam?
You should consider making an appointment if you're experiencing symptoms such as blurred vision, eye pain, flashes, a sudden increase in floaters, or a loss of vision.
How often should we get our eyes checked?
Children and adults should have their vision tested regularly. The frequency can vary based on age, health, and risk of developing eye issues like cataracts or macular degeneration.
Is there any discomfort involved in an eye exam?
Most tests are painless. However, some may find the bright light uncomfortable during pupil dilation and the puff of air in the eye pressure test slightly startling.
| Test | Objective | Comfort |
|---|---|---|
| Visual acuity | To measure clarity of vision | Comfortable |
| Refraction test | To determine the need for corrective lenses | Comfortable |
| Pupil dilation | To examine the interior structure of the eye | Slightly uncomfortable due to brightness |
| Eye pressure | Checks for glaucoma | Momentarily startling |
| Phoropter | Fine-tunes lens prescription | Comfortable |
| Visual field test | Assesses peripheral vision | Comfortable |
| Autorefractor | Provides an objective measurement of refraction | Comfortable |
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address some of the most common queries related to the timeframe associated with various aspects of eye examinations.
What is the duration of an eye exam at national retail chains like Walmart or LensCrafters?
Eye exams at national retail chains generally take approximately 20 to 30 minutes. This timing can vary, however, based on the complexity of the individual's vision requirements and the store's customer flow.
After completing an eye examination, how long does it typically take to receive prescription glasses?
The standard wait time for prescription glasses is about one to two weeks. Some retailers may offer same-day service for certain prescriptions and frame selections.
What is the expected time to get contact lenses following an eye examination?
After an eye exam, the timeline for receiving contact lenses can be immediate if in-stock, or it may take one to two weeks for custom or special orders.
How many minutes or hours can the effects of eye dilation be expected to last?
The effects of eye dilation typically last between 4 to 6 hours. Individual experiences may vary, and some may find that the effects diminish sooner or last longer.
Can I safely operate a vehicle immediately after having an eye examination?
We advise against driving immediately after an eye examination if your eyes were dilated, as this can temporarily impair your ability to focus and make bright lights more glaring.
What's the duration of a standard eye exam that includes the process of pupil dilation?
An eye exam that includes dilation may take longer. Generally, it lasts about 30 to 60 minutes.
You should also account for the additional time it takes for the effects of dilation to wear off.
How much does an Eye Exam Cost ?
To clarify, the cost of an eye exam can range widely. It can be as little as $50 at a retail store to over $250 for an exam conducted by a specialized ophthalmologist. Learn more here in our article How Much Does an Eye Exam Cost

